[윤성우의 열혈 Java 프로그래밍] Chapter 06 - 메소드에 대한 이해와 정의
카테고리: Java lang
태그: java
06-1. 메소드에 대한 이해와 메소드의 정의
- 메소드의 동작
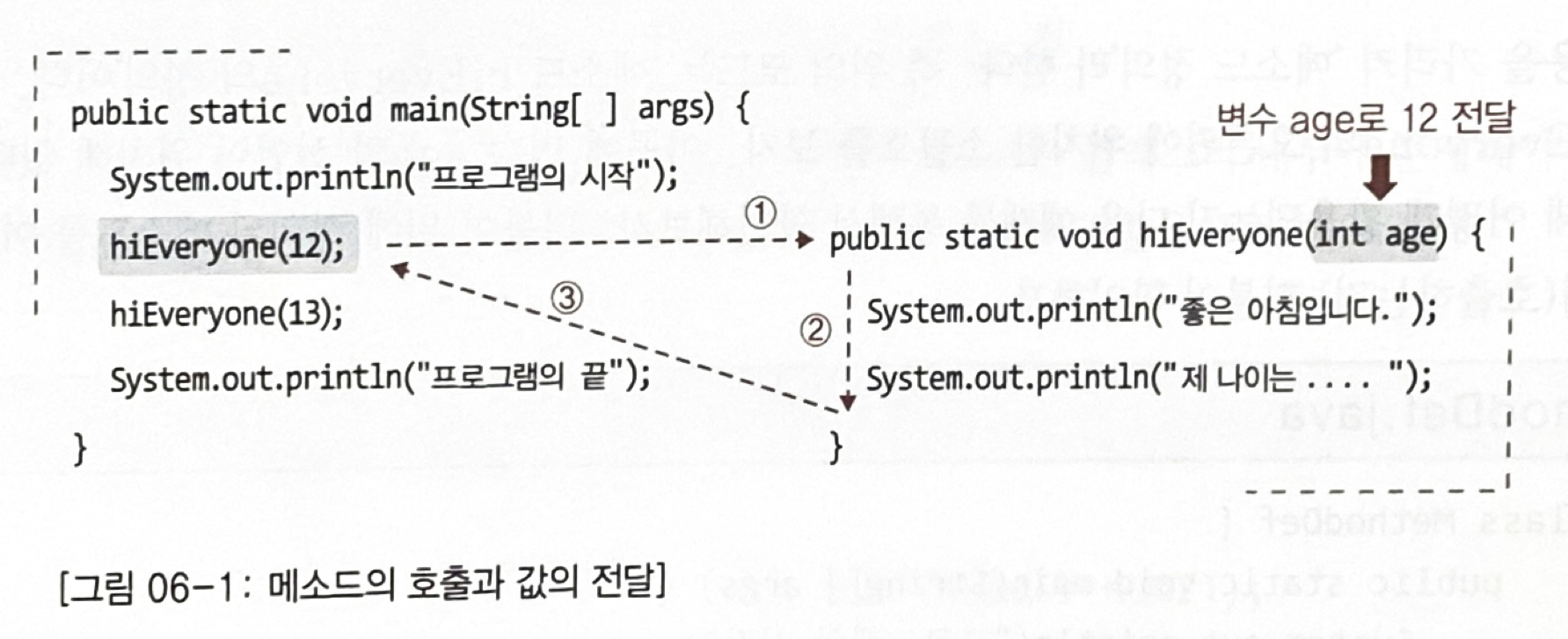
public class MethodDef {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("프로그램의 시작");
hiEveryone(26);
System.out.println("프로그램의 끝");
}
public static void hiEveryone(int age) {
System.out.println("좋은 아침입니다.");
System.out.println("제 나이는 " + age + "입니다.");
}
}
- 값을 반환하는 메소드

public class MethodReturns {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result;
result = adder(4,5);
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(square(3));
}
public static int adder(int a, int b) {
int addResult = a+b;
return addResult;
}
public static double square(double a) {
return a*a;
}
}
06-2. 변수의 스코프
지역변수(Local Variable)는 선언된 지역을 벗어나면 메모리 공간에서 소멸된다.

06-3. 메소드의 재귀 호출
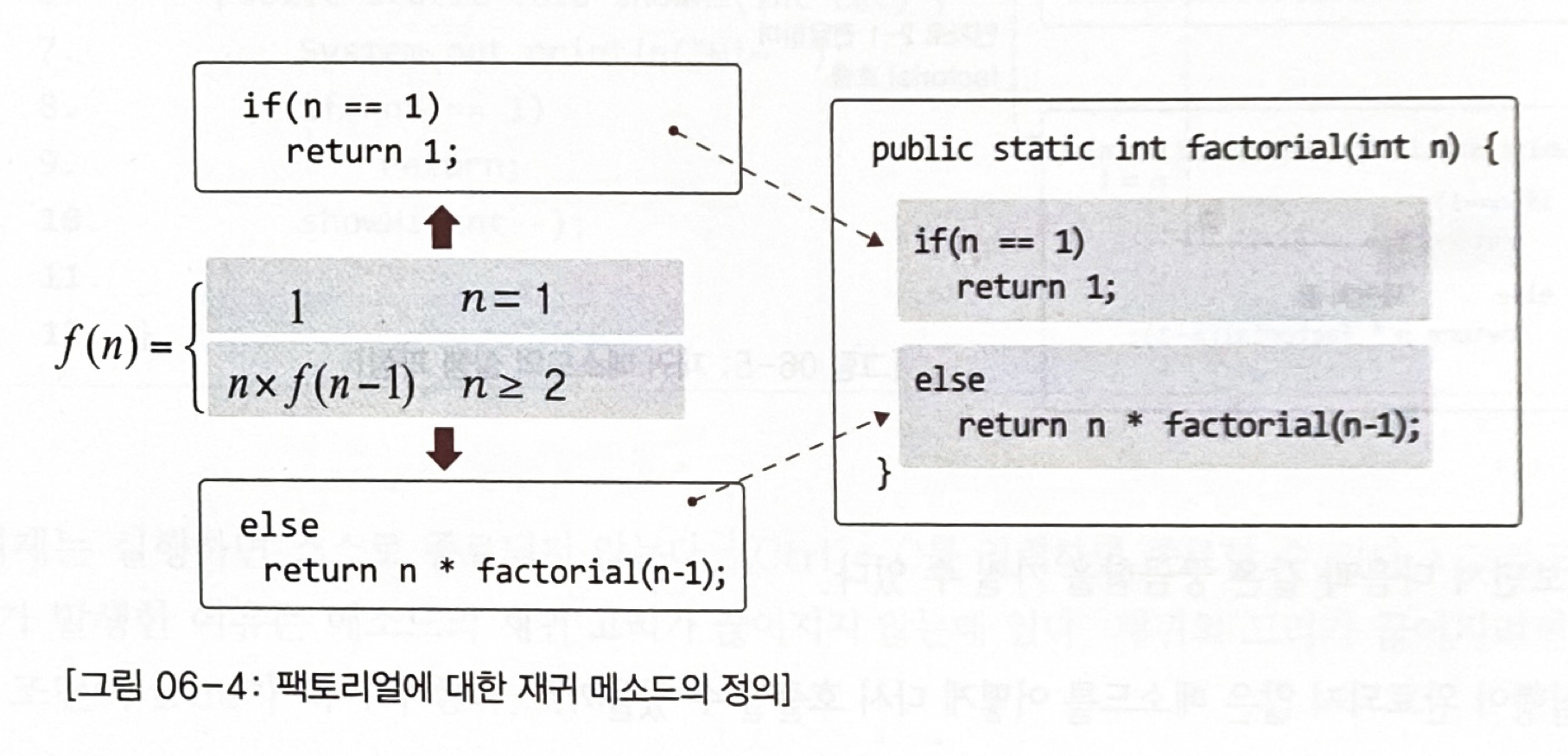
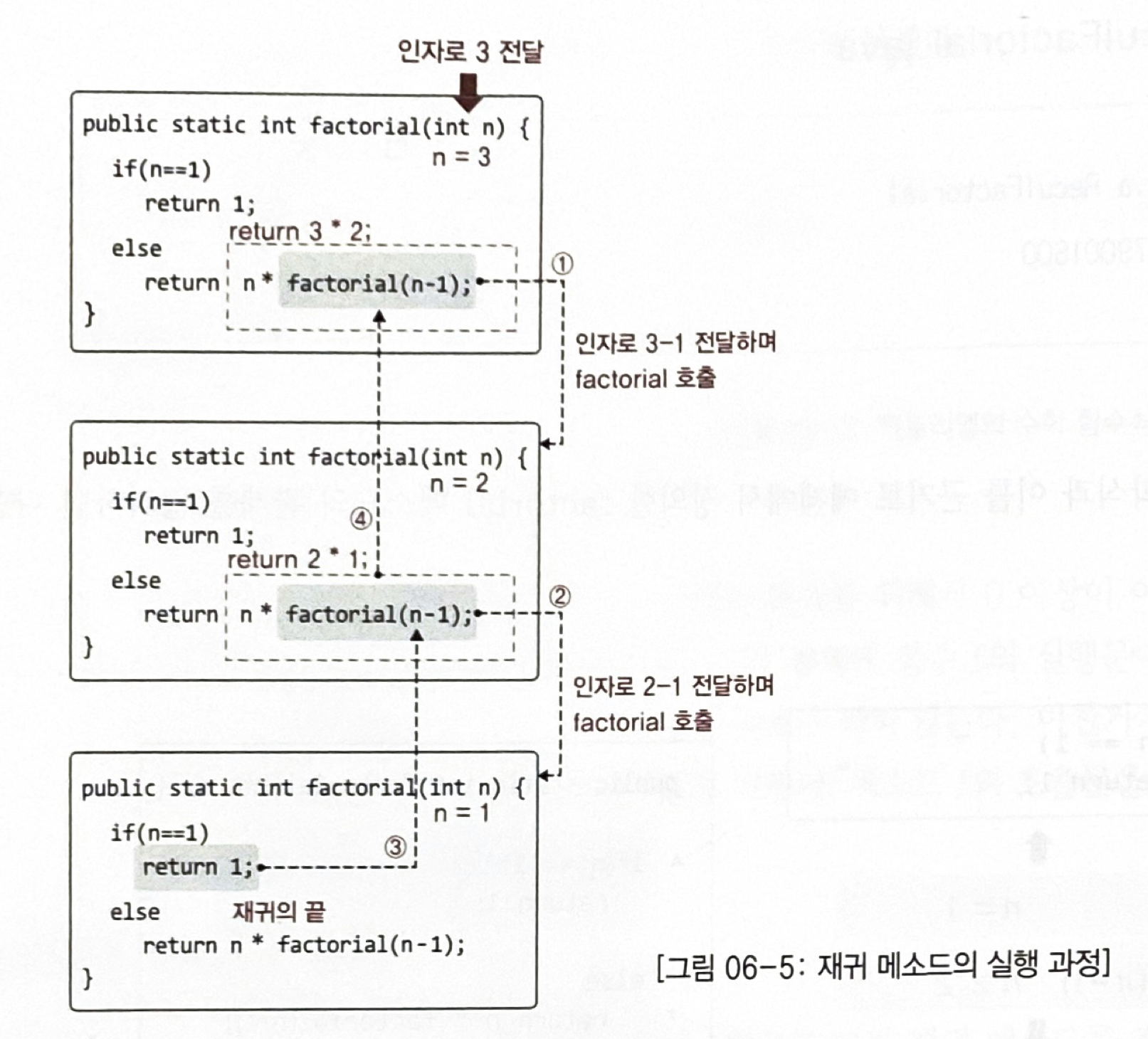
public class ReculFactorial {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("3 factorial: "+factorial(3));
System.out.println("12 factorial: "+factorial(12));
}
public static int factorial(int n){
if(n == 1)
return 1;
else
return n*factorial(n-1);
}
}
(주의) 종료 조건을 꼭 설정해야한다. 안 하면 재귀문을 탈출할 수 없다.
public class InfRecul {
public static void main(String[] args) {
showHi(3);
}
public static void showHi(int cnt) {
System.out.println("Hi~ ");
if(cnt == 1)
return;
showHi(cnt--); // cnt의 값이 전달된 다음에 cnt의 값이 감소한다. 따라서 재귀문을 탈출할 수 없다.
// showHi(--cnt); // 이렇게 써줘야 함
}
}

댓글 남기기